There are many questions concerning the ionosphere and its layers in US license exams.

Experienced hams talk about the ionosphere a lot these days and we see plenty written on the topic in amateur radio websites and magazines. So what’s the importance of the ionosphere?
The real magic in ham radio is skywave propagation where signals can travel well beyond line of sight, even to the other side of the planet if conditions are right. We can have two-way radio communication between Iceland and Australia and places in between because voice, video and data signals may be bent back to earth by the ionosphere.

The ionosphere is shell of electrons and electrically charged atoms and molecules (ions) that surrounds the Earth, stretching from a height of about 50 km (31 mi) to more than 1,000 km (620 mi). Because this band is electrically active the ionosphere is able to reflect or refract electromagnetic radiation at certain frequencies, the HF bands in particular. For most hams communicating beyond line of sight is a big deal and the ionosphere is what makes long distance (DX) contacts commonplace.
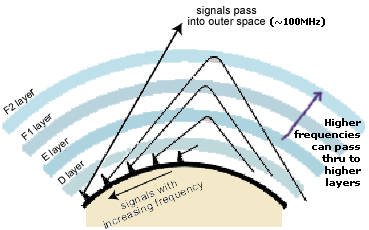
There are two defined ionospheric layers at night and four in daytime, the difference being exposure to the sun which provides most of the energy to the ionosphere.
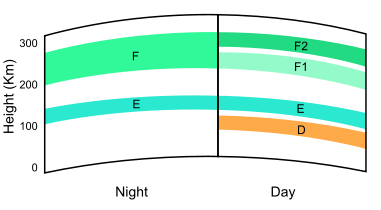
In daylight the F layer separates into F1 and F2 regions. Because F2 is farthest from the earth’s surface it can bend radio waves the greatest distance.

Long-distance propagation changes with day/night cycles and seasonal variance away from the equator. There are numerous anomalies and disturbances that can affect the ionosphere. Between all these factors the ionosphere is not a uniform shell; it has varying height, thickness, and density. This continually changing area makes HF propagation highly variable.
Also known as skip, ionospheric propagation of shortwave (HF) radio signals travel a specific radius or skip distance from the transmitting antenna. This makes received signals particularly strong at the skip distance.

In addition to single skip distance, the earth itself can reflect/refract signals from the ionosphere back up, resulting in a secondary skip or hop and perhaps Continue reading
